Understanding HS Codes: How Updates Impact Global Trade and Market Analysis
Over 98% of global trade depends on accurate HS code classification—missing an update could cost you significantly. At the Observatory of Economic Complexity (OEC), we're here to keep you informed and help you make smart decisions in today's international markets.
HS codes are essential for classifying products and analyzing trade data. Every five years, the World Customs Organization updates these codes to reflect market changes and new technologies. Missing these updates can lead to misclassified products, compliance issues, and flawed market insights.
Recognizing these challenges, we at the OEC make complex trade data accessible. Each HS code revision presents obstacles—products get reclassified, and comparing data over time becomes tricky. In this post, we'll explore why HS codes are crucial, how updates affect trade analysis, and how the OEC helps you navigate these changes confidently.
The Changing Face of HS Codes
HS codes are the backbone of international trade classification. They are structured hierarchically, allowing for detailed and precise categorization of products:
- Chapters (2 digits): Broad categories (e.g., “01” for live animals).
- Headings (4 digits): More specific groups within chapters (e.g., “0101” for horses).
- Subheadings (6 digits): Even more detailed classifications (e.g., “010121” for purebred breeding horses).
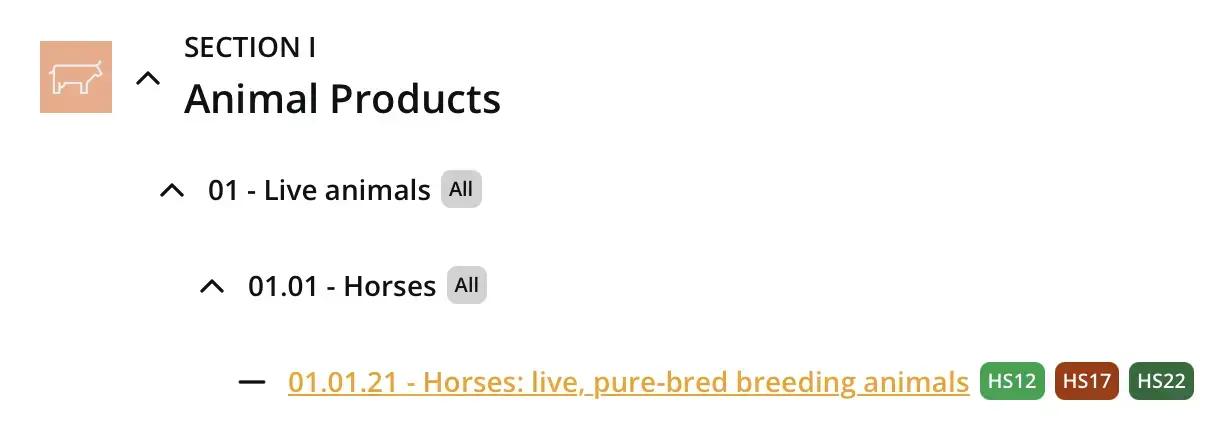
Countries often extend HS codes beyond six digits to accommodate more specific national requirements. For example, the United States uses 10-digit codes known as the Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS), while the European Union uses 8-digit codes.
This hierarchical structure allows for both global standardization and national specificity, facilitating international trade while meeting individual country needs.
Country-Specific Classifications and Other Systems
While the HS code system is widely adopted, some countries use additional classification systems:
- Germany’s EGW (Einheitliches Güterverzeichnis für den Verkehrssektor): A classification for goods in the transport sector.
- France’s (Classification des Produits Français): A system for classifying products according to economic activities in France.
- Italy’s ATECO: Used for economic activities classification.
In addition to country-specific systems, the Standard International Trade Classification (SITC) classifies products by economic function, making it useful for long-term trade analysis and comparisons across time periods.
At the OEC, we accommodate these variations by providing access to multiple classification systems. You can access data using different HS code revisions through our tools, like the global rankings for the Economic Complexity Index, and use SITC to explore the historical changes in international trade during the last decades in the Viz Builder.
Additionally, we work on ensuring data consistency across the platform. For example, when we map different HS classifications to a common framework to enable seamless analysis of economic complexity.
The Smartphone Evolution
Smartphones have become an essential part of daily life, but they didn’t have their own specific HS code until the 2022 revision. Before this, they were classified under broader categories like HS 851712, alongside other wireless devices. This made it difficult for businesses to track smartphone-specific trade trends accurately.
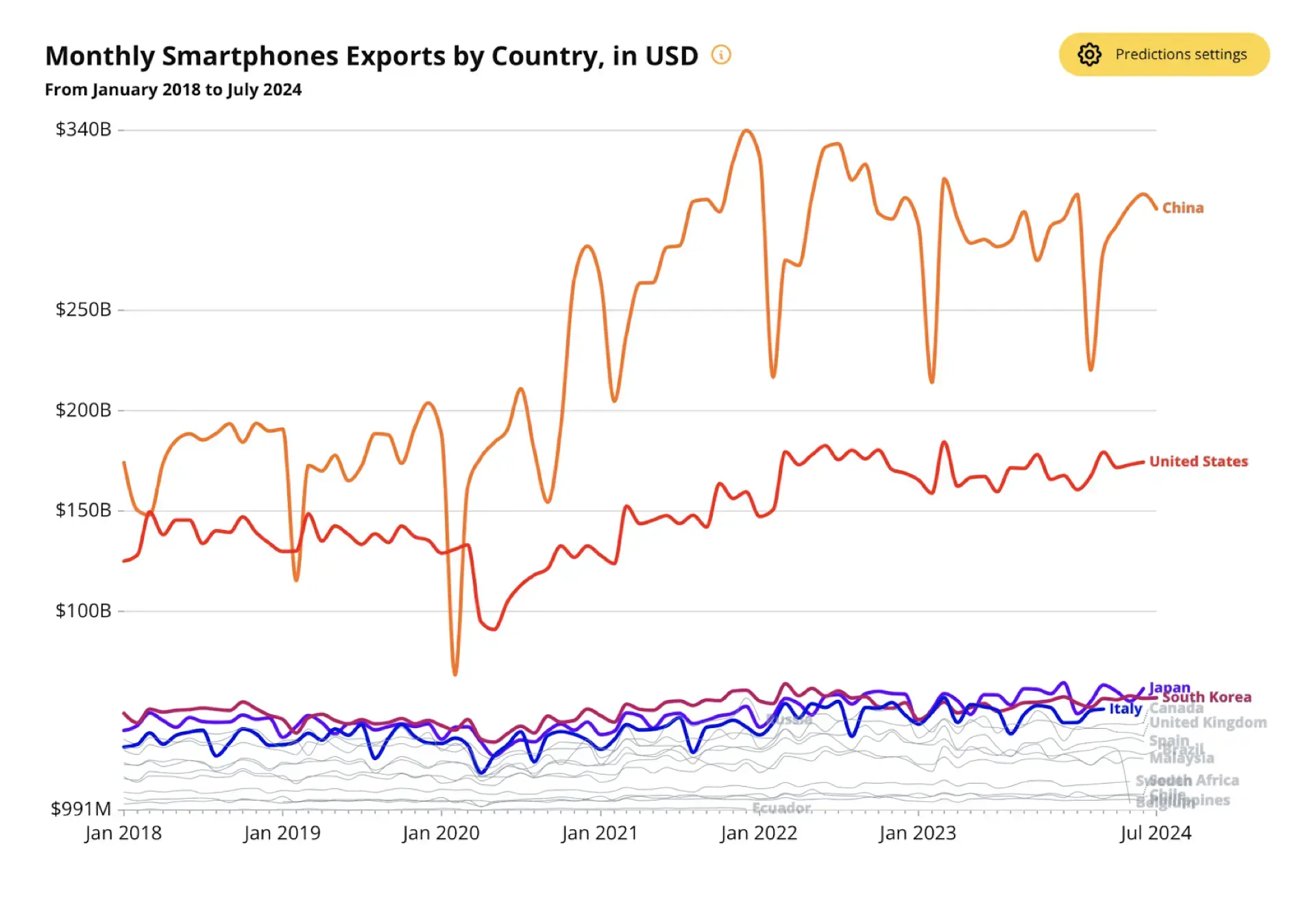
With the 2022 update, HS 851713 was introduced specifically for smartphones, allowing for clearer trade data and market insights. Think about it: your phone isn’t just for calls anymore. It’s your camera, GPS navigator, fitness tracker, and so much more. This change helps businesses make informed decisions, but comparing historical data with this new classification can be tricky.
At the OEC, we simplify this process by standardizing and updating data across revisions, helping you track smartphone trade trends seamlessly, regardless of classification changes.

Emerging Technologies: Drones and Electric Vehicles
Emerging technologies like drones and electric vehicles (EVs) are rapidly reshaping industries and disrupting traditional trade classifications. Their significant market expansion requires up-to-date HS codes for precise trade tracking.
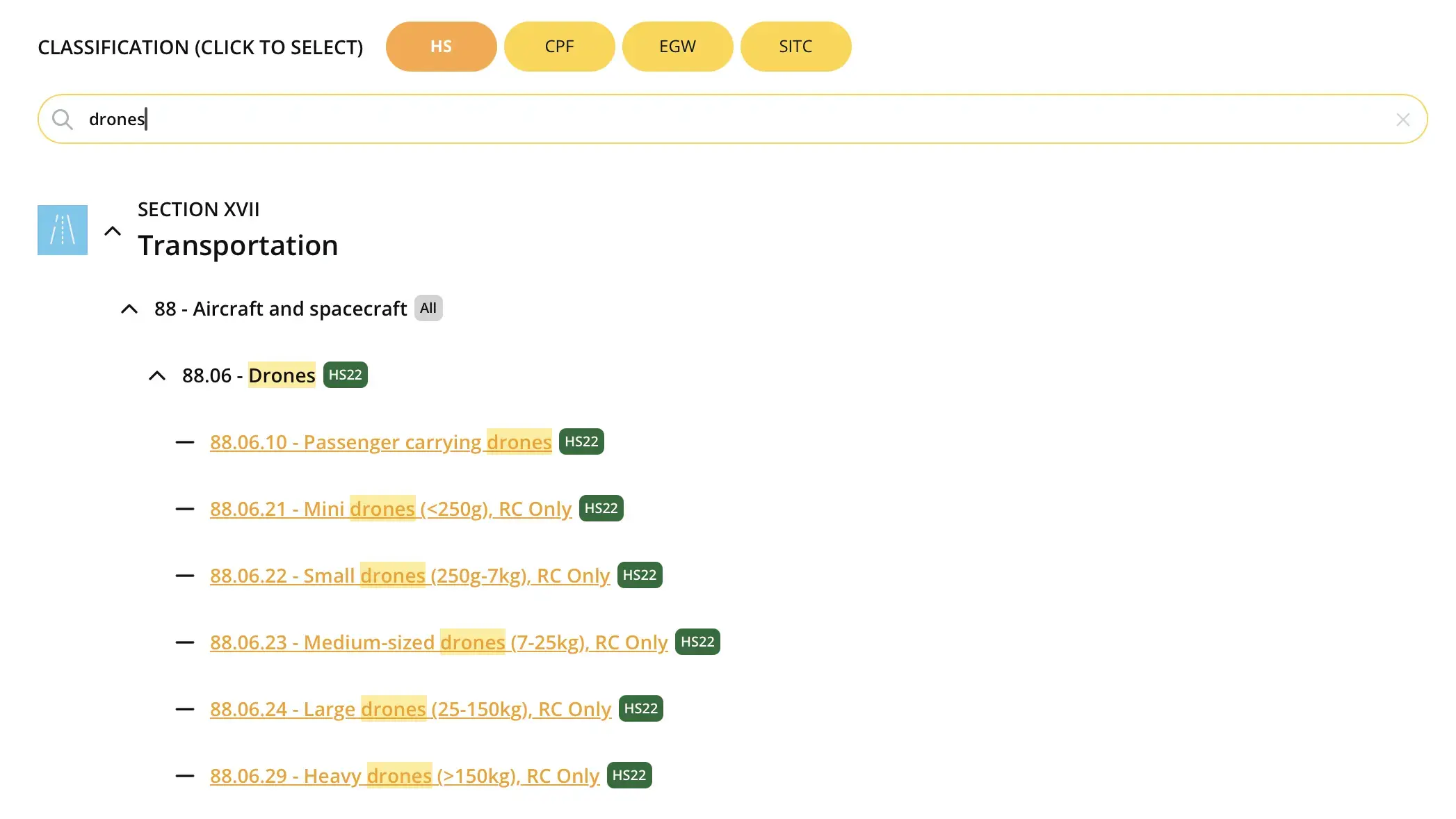
Drones
Drones, used across industries—from recreational use to logistics—present classification challenges. Before 2022, they were spread across categories such as telecommunications equipment, aircraft, and toys. With the 2022 HS update, HS 8806 was introduced specifically for uncrewed aircraft, helping to standardize their classification. However, different uses and components can still complicate trade data analysis.
Electric Vehicles
Similarly, the electric vehicle market is booming, with global EV sales surpassing 14 million units in 2023. Updated HS codes, like HS 850760 for lithium-ion batteries, allow for better tracking of EV components. Yet, as the industry grows, misclassifying parts can lead to disruptions in supply chains and inaccurate market insights.

At the OEC, we provide standardized and updated trade data across these emerging technologies, helping businesses navigate classification changes and stay ahead of market trends.
How We Keep Up with HS Code Changes
At the OEC, we stay ahead of HS code updates to ensure our users have access to accurate, up-to-date trade data. Here’s how we do it:
- Tracking Updates: We monitor changes through official sources like the World Customs Organization (WCO) and the WTO’s HS Tracker to keep our data current.
- Updating Data Models: Every time an HS code revision occurs, we update historical data, models, and visualizations to ensure consistency and accuracy over time.
Spotting Trends: Beyond tracking updates, we use HS code changes to identify emerging markets and technologies. New classifications, like those for electric mobility and drones, often signal growing industries worth watching.
To stay informed, bookmark our HS master table and sign up for our Newsletter for timely alerts on major updates and revisions.
HS Codes vs OEC HS IDs
Anyone who has used our API at the OEC may have noticed a slight difference between the HS product ID found in the API vs the actual WCO HS codes. The reason for this slight difference is that we append the HS Section code to the beginning of our IDs, which is typically published as a roman numeral. Let's take a look at an example:
HS Code 870380 corresponds to Electric motor vehicles. What this code doesn't tell us is that HS chapter 87 (leading 2 digits) falls under Section XVII "Vehicles, Aircraft, Vessels and Associated Transport Equipment".

For this reason, in our API the product ID we use to identify this product is 17870380. The first 2 leading digits are used to signify the section, an important and useful piece of information for anyone trying to group products together hierarchically.
Wrapping Up: Staying Ahead in a Changing Trade World
HS code revisions may seem technical, but they have significant implications for businesses, policymakers, and researchers. Staying current with these updates is essential to avoid costly misclassifications and seize new opportunities.
At the OEC, we simplify this process by providing accurate, up-to-date trade data and tools that keep you ahead of emerging trends. With resources like our HS master table and regular updates, you can make informed, strategic decisions in today’s fast-paced global market.
Stay informed by bookmarking our tools and subscribing to our newsletter—you'll always have the latest insights at your fingertips.
